Member-only story
How to Create Trusted Self-Signed SSL Certificates and Local Domains for Testing
Set up local test domains and enable a trusted, self-signed certificate for quick, local testing

Most of the time, we’ll have domains other than the localhost to test the applications locally, and we’ll also need trusted self-signed SSL certificates.
Self-Signed Certificate
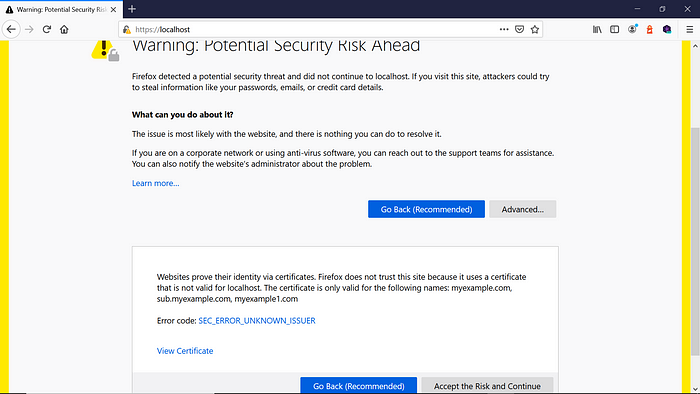
A self-signed certificate is a certificate that’s signed by the person creating it rather than a trusted certificate authority. The development servers can be enabled with self-signed certificates that’ll help us reduce the certificate cost and also the management overheads.
By default, the self-signed certificate throws a certificate-validation error when accessing the websites in browsers but will allow us to proceed to the actual pages by accepting the risk. In some cases, the self-signed certificates won’t help us test some of the browser functionalities that only work through valid SSL — e.g., testing different browsers’ APIs, like geolocation.