Member-only story
Shallow Copy vs. Deep Copy in Python
Understand how copying works in Python with helpful examples
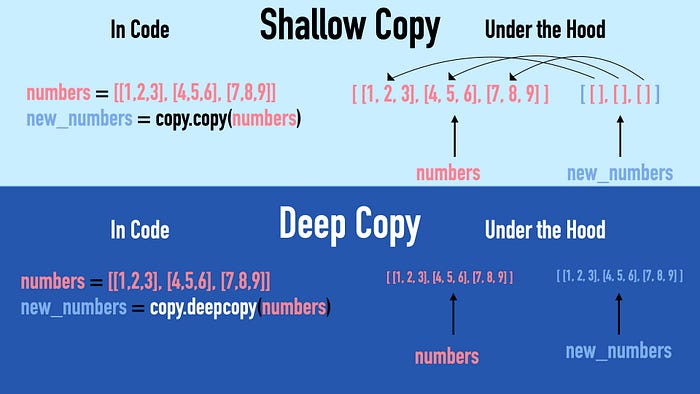
In Python, a shallow copy is a “one-level-deep” copy. The copied object contains references to the child objects of the original object.
A deep copy is completely independent of the original object. It constructs a new collection object by recursively populating it with copies of the child objects.
Copying or Not
In Python, you might use the = operator copy of an object. It is tempting to think this creates a new object, but it doesn't. Instead, it creates a new variable that refers to the original object. This means changing a value in the copied object changes the value of the original object as well.
Let’s use lists to demonstrate this:
Output:
numbers: [100, 2, 3]
new_numbers: [100, 2, 3]
