Member-only story
Python Parameters and Arguments Demystified
Everything you need to know about parameters, arguments, and their types in Python
What are parameters and arguments? Most of the time we use the terms interchangeably — and that’s fine. However, it’s important that you understand the difference between the two. In this article, we’ll explore them in detail. Along the way, you’ll learn all you need to know about parameters and arguments in Python.
Note: If any of the features discussed below give syntax errors, please ensure you’re using a recent version of Python — 3.8 or 3.9.
Parameters and Arguments
Parameters
Parameters are the names that appear in the function definition. In the example below, name, age, and skill are the parameters as they appear in the function definition.
def my_func(name, age, skill):
pass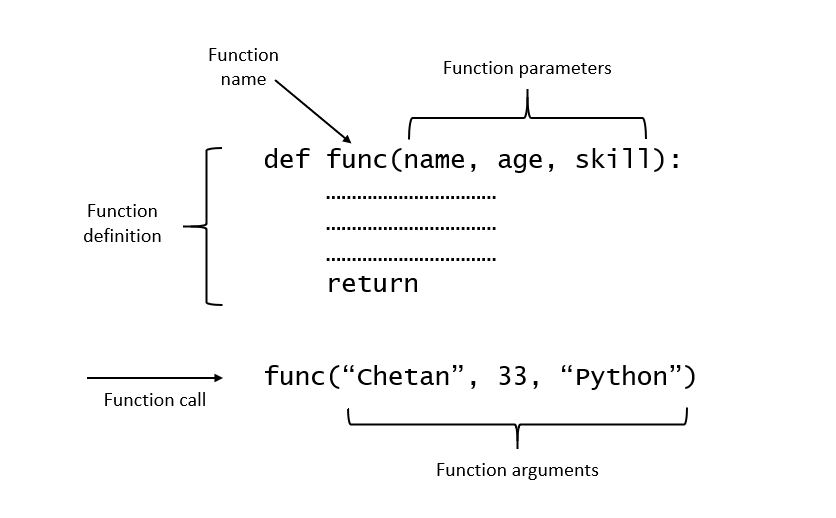
Arguments
Arguments are the names that appear in the function call. In the below example, ‘Chetan’, 33, and ‘Python’ are the arguments as they appear when making a call to the function my_fync.
my_func('Chetan', 33, 'Python')Types of arguments
There are two types of arguments. In the next section you will see how these arguments work, with examples, but first, let’s explore the syntax.
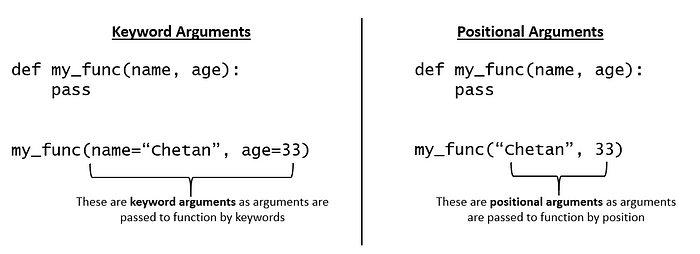
Keyword arguments
Keyword argusment is preceded by identifier/variable in the function call. In the above example, "chetan" and 33 are the keyword arguments. As you can see, they’re preceded by identifiers name and age. Keyword arguments follow key=value pairs syntax. These are also called named arguments.