Building GraphQL Server Using Schema-first Approach in Python
Handle CRUD operations with ease
Schema-first approach is nothing but we first define the schema for our GraphQL service and then we implement the code by matching the definitions in the schema we defined.
We will be using the Ariadne library for this.
Ariadne is a Python library for implementing GraphQL servers using schema-first approach. — ariadne
Overview of the Project
We are going to build the GraphQL server that handles the CRUD operation of Book in the Book Store.
Simply, we will be storing the book's information in our database. To make this project simpler I haven’t used any kind of database just used an in-memory store and focused more on the GraphQL part.
Server Operations
- Add books
- Get book by ID
- List books by genre
- List all the books
- Update the book
- Delete the book
Building the GraphQL Server
Library installation
We highly depend on the Ariadne library, so we have to install that.
pip install ariadneWe have to make our GraphQL server the HTTP server that would receive the HTTP requests, execute GraphQL queries, and return responses.
For this, we can use an ASGI (Asynchronous Server Gateway Interface) server like uvicorn.
pip install uvicornDefining our schema
I invite you to define the schema and implement the code in your own way and requirement. Here we will see my way of defining the schema.
I planned to have some GraphQL object types that can hold some information about the Books in our Book store.
Here I have 2 Object types and 1 enum type as of now to describe a Book.
Book type has the below fields:
title— String type and nonnullablebook_id— ID typegenre— enum typeauthor— array ofAuthortypes and non-nullable
Author type:
- name — String type and non-nullable
- mail — String type
BookGenre enum type:
- has two values (
FICTION,NONFICTION)
The above types are the basic types to handle the Books information.
Now we move forward to define the entry point for our GraphQL service.
Query type
I have the above Query type that has 3 fields.
book— get the book details by providing thebook_idin the argumentbooks— get the list of available booksgetbooks— get the list of books for the requested genre. Thegetgenreargument is an optional one, it has the default value ofFICTION.
type GetBookResult{
isexists: Boolean!
book: Book
}The GetBookResult type has 2 fields:
isexists— Boolean type and non-nullable, tells whether the book information exists or not for the givenbook_id- book
Mutation type
Mutation type has 3 fields
add_book— to create a book resource in our Book store by providing the inputs and the response is the status of that request.update_book— updates the existing book information and the response is the status of that request.delete_book— deletes the book with the given book id and returns the status of the operation.
The above types are used in the add_book field of the Mutation type.
The UpdateInput and the PutStatus types are used in the update_book field of the Mutation type.
type DeleteStatus{
iserror: Boolean!
description: String
}DeleteStatus type is used in the delete_book field of the Mutation type.
We came to the end of our Schema definition. Moving to implement the code.
GraphQL server implementation
In-memory store
As I mentioned earlier I will be using an in-memory data store (simply a variable) to store the book’s information.
BOOK_STORE = [
{
"title": "Book 1", "book_id": 1, "genre": "FICTION",
"authors": [{"name": "Logesh", "mail": "logesh@domain.com"}]
},
]Here I have an initial mock data.
Boilerplate code
We can load our schema in two ways:
- by defining our schema in a variable
- by defining our schema in a separate
.graphqlfile
For example, in the first case:
from ariadne import QueryType, gql, make_executable_schema, MutationTypefrom ariadne.asgi import GraphQLtype_defs = gql("""
type Query {
book(book_id : ID!): GetBookResult
books: [Book]
}
""")query = QueryType()
mutation = MutationType()schema = make_executable_schema(type_defs, query, mutation)
app = GraphQL(schema, debug=True)
For the second case:
from ariadne import QueryType, make_executable_schema, MutationType, load_schema_from_pathfrom ariadne.asgi import GraphQLquery = QueryType()
mutation = MutationType()book_type_defs = load_schema_from_path("book_schema.graphql")
schema = make_executable_schema(book_type_defs, query, mutation)
app = GraphQL(schema, debug=True)
In the above code, we can see that I have loaded our schema from the external file.
Helper functions
I have written some helper functions like fetching the book information from the BOOK_STORE:
The above function is used to get the book of given ID from the BOOK_STORE variable(our database)
This function is used to check whether the book with the given ID exists or not.
This simple function is used to create a unique id, which is needed while creating a new book.
To delete the book from the BOOK_STORE variable by providing the book ID.
This function is used to get the list of books with the given genre.
Resolvers
Now we are ready to implement our GraphQL Server resolvers.
For the book field of the Query type we have the above function to resolve the query and return the dictionary with the keys(fields) that we mentioned in our response type of this request in the schema.
The above resolver functions is used to resolve the query fields — books and getbooks.
Now moving to the Mutation type.
The above function is used to create a new book in our Book store.
resolve_update_book function is used to update the existing book.
This function is used to delete the book by providing the book id.
Now we have done with our resolvers, moving to serve the clients.
Serving the Clients
By using uvicorn, we are going to make our GraphQL server to serve over HTTP.
Execute the below command to start the server.
uvicorn main:app
# uvicorn <filename>:<GraphQL object>Uvicorn running on http://127.0.0.1:8000
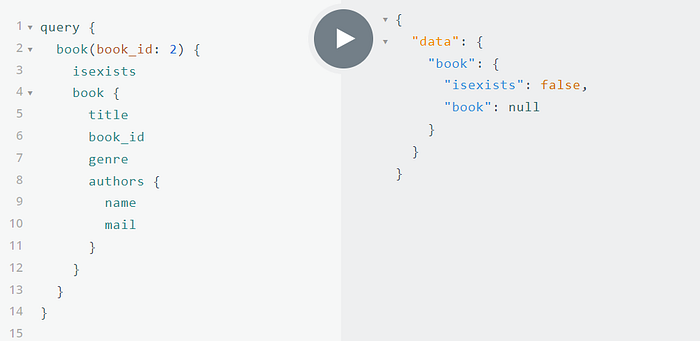
Query book

Mutation add_book
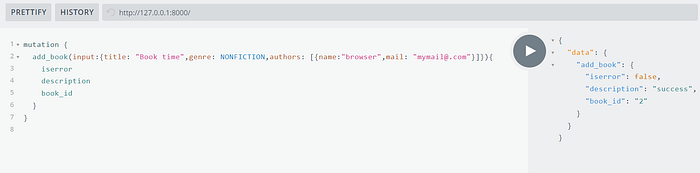
Query books

Mutation update_book

Query book

Query getbooks

Mutation delete_book

Query book
We can also use Postman as the GraphQL client.
In this article, we have seen how to build our own GraphQL server in Python (schema first approach).
You can find this project on my Github. Thanks for reading.